Introduction
In an unpredictable world, businesses face a variety of risks – from natural disasters and cyberattacks to supply chain disruptions and unexpected crises. To not only survive, but thrive during such interruptions, organizations need a proactive approach to safeguard critical processes and maintain business continuity.
This is where Business Continuity Management (BCM) becomes essential. BCM provides a structured framework to ensure that businesses can continue operating with minimal disruption, even in the face of significant challenges.
In this guide, we will provide detailed insights into BCM, covering its definition, key components, operational framework, benefits, implementation strategies, and applicable regulatory standards. Explore why BCM is critical for every organization and how it can help you build operational resilience in an increasingly complex risk landscape.
What is Business Continuity Management (BCM)?
Business Continuity Management (BCM) is a strategic framework that enables organizations to maintain critical processes during and after disruptions. It involves identifying potential risks, assessing their impact, and developing plans to ensure minimal downtime and a swift recovery.

What is Business Continuity Management (BCM)? Source: BSI, “Business Continuity Management, 2023
The primary goal of BCM is to prevent interruptions to essential business processes while also preparing the organization to respond effectively and systematically to crises when they arise. BCM is supported by policies, management systems, and company-wide practices designed to handle all risk scenarios that could threaten the organization’s economic stability and operational continuity.
However, BCM is not just about having a plan – it is about embedding resilience into the organization’s culture. A robust BCM strategy equips organizations to withstand risks and build long-term resilience by expanding risk management, adding crisis and recovery strategy .
Therefore, BCM consists of the following core components:
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks that can disrupt operations and assessing their impact.
- Crisis Management: Coordinate an immediate, structured response to minimize the impact of disruptions.
- Recovery Strategy: Facilitate a smooth return to normal operations after a disruption.
A well-implemented BCM framework empowers organizations to remain operational during crises while safeguarding their reputation, financial health, and stakeholder confidence.
Why is Business Continuity Management important?
Business Continuity Management is a critical factor in ensuring long-term organizational success and stability. When disruptions occur, a well-prepared organization can continue operating with minimal impact, while those without effective continuity strategies risk severe operational and financial setbacks. Effective BCM provides multiple strategic advantages, including:
Minimising Downtime: Ensures critical processes remain operational even during disruptions, reducing both financial losses and operational impact.
Protecting Reputation: Demonstrates readiness and reliability, preserving stakeholder confidence.
Regulatory Compliance: Helps meet standards and legal requirements like ISO 22301, NIS-2, and BSI 200-4.
Enhancing Resilience: Builds an adaptable organization capable of responding effectively to unexpected events.
Competitive Edge: Faster recovery times provide an advantage over competitors struggling to resume operations, strengthening market position and customer retention.
The Key Elements of Business Continuity Management
To implement BCM effectively, organizations must focus on the following core components, each critical for building a robust and responsive continuity strategy:
Risk Assessment
Identify internal and external risks that could disrupt operations, such as natural disasters, IT failures, or economic changes. Prioritize risks based on their likelihood and potential impact.
Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Analyze which processes and resources are most critical to operations. Assess the financial, operational, and reputational impact of disruptions.
Continuity Planning
Develop detailed plans to ensure key business processes can continue during disruptions. Include recovery strategies to restore operations to normal levels as quickly as possible.
Testing and Training
Conduct regular drills and simulations to test the effectiveness of continuity plans. Train employees to understand their roles and responsibilities during crises.
Review and Continuous Improvement
Regularly challenge BCM plans based on lessons learned, emerging risks, and evolving business processes. Monitor changes in the regulatory landscape and strategic priorities of the business to ensure alignment.
These components work together to form a robust foundation for handling unexpected events efficiently.
How does Business Continuity Management function?
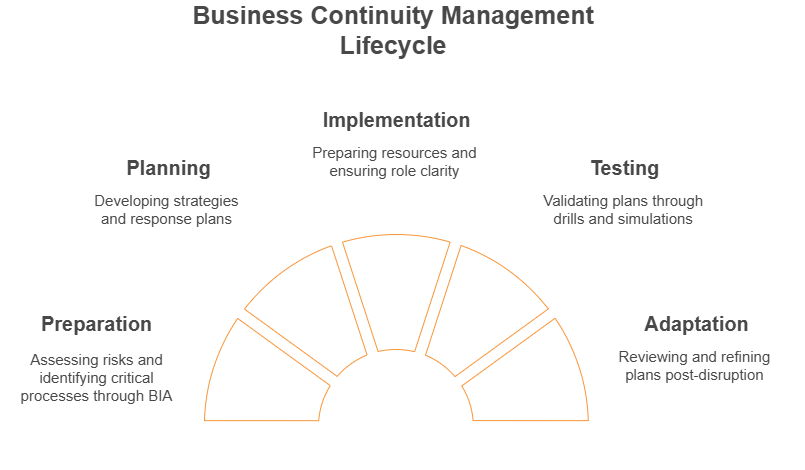
Business Continuity Management operates through a structured, proactive lifecycle with the following stages:
Preparation:
- Assess risks and identifyy critical processes through a Business Impact Analysis (BIA).
- Understand the potential impact of disruptions on operations, finances, and reputation.
Planning:
- Develop continuity strategies and response plans to maintain operations during disruptions.
- Include clear recovery objectives and assign roles to key personnel.
Implementation:
- Equip the organization with the necessary resources, tools, and training to execute plans effectively.
- Ensure all stakeholders understand their roles and responsibilities in a crisis.
Testing:
- Conduct regular drills, simulations, and exercises to validate the effectiveness of continuity plans.
- Identify gaps and areas for improvement to strengthen resilience.
Adaptation:
- After a disruption, review the organization’s response, address identified weaknesses, and refine plans.
- Incorporate lessons learned and stay updated on both emerging risks and regulatory requirements.
Business Continuity Management lifecycle
By following this cycle, BCM ensures organizations can minimize downtime, maintain stakeholder trust, and recover with efficiency and confidence.
BCM Implementation Roadmap
Implementing BCM requires a clear and structured roadmap to ensure a smooth and effective rollout. The following steps outline the essential actions for building a resilient framework:
1. Secure Executive Support
Gain leadership commitment to ensure the allocation of necessary resources, funding, and authority for BCM initiatives.
2. Conduct Risk Identification
Map out internal and external risks that could disrupt operations, such as cyber threats, natural disasters, or supply chain failures.
3. Perform Business Impact Analysis
Determine the priority of business processes and their dependencies. Understand the potential financial, operational, and reputational impacts of disruptions.
4. Develop Continuity Plans
Draft contingency plans for maintaining essential functions during disruptions. Include clear recovery strategies for returning to normal operations.
5. Allocate Resources
Provide teams with the necessary tools, systems, and training to execute continuity plans effectively. Ensure cross-departmental coordination to streamline implementation.
6. Test and Refine
Regularly conduct drills, simulations, and scenario testing to validate plan effectiveness. Revise plans based on testing outcomes to address any identified gaps.
7. Monitor and Improve
Establish a continuous review process to ensure recovery plans remain up to date with emerging risks, regulatory requirements, and business changes.
By following this roadmap, organizations can transform Business Continuity Management from a compliance exercise into a strategic advantage, ensuring preparedness for disruptions, safeguarding critical operations, and fostering long-term resilience.
Which standards are there for BCM?
The regulatory landscape for Business Continuity Management (BCM) is becoming increasingly , reflecting its growing importance across sectors. Standards and regulations like NIS-2, DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act) , BSI-2004, and ISO 22301 set mandatory requirements for many industries.
ISO 22301:
An international standard specifying BCM requirements to manage and reduce risks.
- Established in 2012, ISO 22301 outlines operational measures to maintain or restore operations in the event of incidents.
- Unlike general risk management under ISO 31000, ISO 22301 focuses on actionable BCM measures to ensure continuity and recovery.
BSI-Standard100-4 & 200-4:
Offers guidance on establishing BCM systems with a focus on organizational resilience.
- This standards address synergies between BCM, information security and crisis management to strengthen overall resilience.
- Particularly useful for aligning BCM with broader security frameworks.
NIS-2 Directive:
A European regulation that sets stringent requirements for network and information system security.
- Mandates stricter cybersecurity measures, incident reporting, and business continuity requirements.
Applies to a broad range of critical sectors and essential services to enhance overall cyber resilience across the EU.
DORA:
This regulation specifically focuses on strengthening the operational resilience of financial entities within the EU.
- DORA outlines clear steps for ICT risk management, incident reporting, and testing to ensure operational continuity.
- Aiming to enhance the digital operational resilience of financial entities and their critical third-party service providers.
Aligning your BCM implementation with relevant regulatory standards and industry-specific requirements is essential to avoid fines, protect operational stability, and safeguard your reputation. While these standards provide valuable guidance, building on proven best practices can further streamline implementation, enhance effectiveness, and ensure your organization is prepared to respond to evolving risks.
Note: Ensure your BCM implementation aligns with relevant regulatory standards to avoid fines and reputational damage.
Summary
Business Continuity Management (BCM) is a vital strategic tool for organizations seeking to build resilience in increasingly unpredictable environments. By focusing on risk assessment, business impact analysis, continuity planning, testing, and continuous improvement, BCM enables organizations to minimize downtime, protect their reputation, and ensure sustained operations.
BCM is no longer a best practice – it has become a necessity for organizations committed to thriving in the face of uncertainty. Start strengthening your business continuity today to secure your organization’s future.